Fixed point 定点数计算
Solidity 中的定点运算(以 Solady、Solmate 和 ABDK 为例)
定点数是仅存储分数分子的整数,而分母是隐含的。
在大多数编程语言中,这种类型的运算是不必要的,因为它们有浮点数。但在 Solidity 中,这种运算是必要的,因为 Solidity 只有整数,而我们经常需要对小数进行运算。
大多数 DeFi 智能合约中都有定点数,因此了解它们是必须的。
例如,如果“隐含分母”是 100,则保留“10”的定点数将被解释为 $\frac{10}{100} = 0.1 $。
Solidity 中最常见的定点数是 $10^{18}$ ,以太坊和大多数 ERC-20 代币的“小数”数量。当我们读取以太坊地址的余额时,我们会隐式地将该数字除以 $10^{18}$ 确定其 Ether 数量。
例如,一个地址的余额为 $10^{19}$ 被解释为有 10 个 Ether — 因为除以 $10^{18}$ 是隐含的。
分母为 $10^{18}$ 非常常见,Solidity 社区的工程师将其称为“Wad”(该名称最初由 MakerDAO 引入)。有时,18 位定点数被解释为将最右边的 18 位数字分配给小数,例如,数字“10”如下所示:
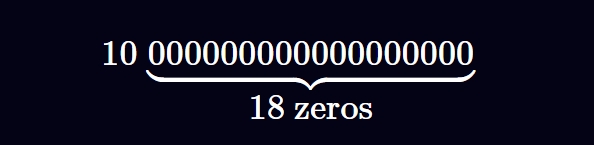
将整数转换为定点数
要将整数转换为定点数,请将整数乘以隐含的分母。例如,2 Ether 是 $2 * 10^{18}$
定点数乘法
要将两个定点数相乘,我们遵循分数乘法的规则:
- 将分子相乘
- 将分母相乘
- 简化结果。
例如:$\frac{x}{d} * \frac{y}{d} = z $,其中
x,y表示 定点数,d表示分母,z表示将定点数相乘的结果转成整数
如果我们想把定点数相乘的结果也转化成定点数的话,整式结果需要乘以分母,即 z * d
继续化简为: $z * d = \frac{x}{d} * \frac{y}{d} * d = \frac{x * y}{d} $
乘以定点的代码示例
Solady 库有一个 mulWad 数学运算,可以将两个定点数与隐含的 Wad 分母相乘($10^{18}$)。下面,我们展示代码,然后解释它与我们之前的讨论有何关联:
/// @dev The scalar of ETH and most ERC20s.
uint256 internal constant WAD = 1e18;
/*´:°•.°+.*•´.*:˚.°*.˚•´.°:°•.°•.*•´.*:˚.°*.˚•´.°:°•.°+.*•´.*:*/
/* SIMPLIFIED FIXED POINT OPERATIONS */
/*.•°:°.´+˚.*°.˚:*.´•*.+°.•°:´*.´•*.•°.•°:°.´:•˚°.*°.˚:*.´+°.•*/
/// @dev Equivalent to `(x * y) / WAD` rounded down.
function mulWad(uint256 x, uint256 y) internal pure returns (uint256 z) {
/// @solidity memory-safe-assembly
assembly {
// Equivalent to `require(y == 0 || x <= type(uint256).max / y)`.
if gt(x, div(not(0), y)) {
// x * y > type(uint256).max
if y { // y != 0
mstore(0x00, 0xbac65e5b) // `MulWadFailed()`.
revert(0x1c, 0x04)
}
}
z := div(mul(x, y), WAD)
}
}
假设一个用户有 1 DAI(有 18 位小数),我们希望计算他们的余额,假设他们的存款获得了 15% 的利息。这是一个需要定点运算的明显例子,因为我们不能在 Solidity 中直接将一个数字乘以 1.15。
import "https://github.com/Vectorized/solady/blob/main/src/utils/FixedPointMathLib.sol";
contract C {
using FixedPointMathLib for uint256;
uint256 tokenBalance = 1e18;
function compute15PInterest() public view returns (uint256) {
return tokenBalance.mulWad(1.15e18);
} // 1150000000000000000
}
定点数除法
要将两个定点数相除,我们遵循分数除法的规则:
-
反转除数,将除法变成乘法
-
将分子相乘
-
将分母相乘
-
简化结果。
-
例如:$\frac{x}{d} / \frac{y}{d} = \frac{x}{d} * \frac{d}{y} = z $,其中
x,y表示 定点数,d表示分母,z表示将定点数相乘的结果转成整数
如果我们想把定点数相除的结果也转化成定点数的话,整式结果需要乘以分母,即 z * d
继续化简为: $z * d = \frac{x}{d} * \frac{d}{y} * d = \frac{x * d}{y} $
/// @dev Equivalent to `(x * WAD) / y` rounded down.
function divWad(uint256 x, uint256 y) internal pure returns (uint256 z) {
/// @solidity memory-safe-assembly
assembly {
// Equivalent to `require(y != 0 && x <= type(uint256).max / WAD)`.
if iszero(mul(y, lt(x, add(1, div(not(0), WAD))))) {
mstore(0x00, 0x7c5f487d) // `DivWadFailed()`.
revert(0x1c, 0x04)
}
z := div(mul(x, WAD), y)
}
}
加定点数
要将两个定点数相加,我们遵循加减法的规则:
-
分母不变
-
将分子相加
-
简化结果。
-
例如:$\frac{x}{d} + \frac{y}{d} = \frac{x + y}{d} = z $, 其中
x,y表示 定点数,d表示分母,z表示将定点数相乘的结果转成整数
如果我们想把定点数相除的结果也转化成定点数的话,整式结果需要乘以分母,即 z * d
继续化简为: $z * d = \frac{x + y}{d} * d = x + y $
减定点数
要将两个定点数相减,我们遵循加减法的规则:
-
分母不变
-
将分子相减
-
简化结果。
-
例如: $\frac{x}{d} - \frac{y}{d} = \frac{x - y}{d} = z $, 其中
x,y表示 定点数,d表示分母,z表示将定点数相乘的结果转成整数
如果我们想把定点数相除的结果也转化成定点数的话,整式结果需要乘以分母,即 z * d
继续化简为: $z * d = \frac{x - y}{d} * d = x - y $
二进制与十进制定点数
二进制定点数是分母可以表示为 $2^{n}$
二进制定点数通常用 Q 符号表示。例如,UQ112x112 使用 $2^{112}$ 作为分母。U 表示“无符号”。用于保存 UQ112x112 的数据类型为 uint224: $2^{112} * 2^{112} = 2^{224}$。
另一个例子是,UQ64x64(或 UQ64.64)将 uint128 “小数部分”保存在最低有效 64 位中,将“整数”保存在最高有效位中。
二进制定点数的优点是我们可以使用节省 gas 的左/右位移位而不是乘以分母(将整数转换为定点数时,或在除法时进行右位移位)。
举个基本的例子,考虑以下情况:
2的二进制表示形式为1016的二进制表示形式为1000016 = 2 *$2 ^ {3}$, 二进制表示为:10000 = 10 << 3
二进制运算如下:
x * $2 ^ {112} == x << 112
x / $2 ^ {112} == x >> 112 , x 可以是任意数字,只要它适合无符号整数。
ABDK 库
ABDK 库 fromUInt 函数代码将 int256 的值转成 Q64.64 = int128 类型
function fromInt (int256 x) internal pure returns (int128) {
unchecked {
require (x >= -0x8000000000000000 && x <= 0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF);
return int128 (x << 64);
}
}
/**
* Convert signed 64.64 fixed point number into signed 64-bit integer number
* rounding down.
*
* @param x signed 64.64-bit fixed point number
* @return signed 64-bit integer number
*/
function toInt (int128 x) internal pure returns (int64) {
unchecked {
return int64 (x >> 64);
}
}
/**
* Convert unsigned 256-bit integer number into signed 64.64-bit fixed point
* number. Revert on overflow.
*
* @param x unsigned 256-bit integer number
* @return signed 64.64-bit fixed point number
*/
function fromUInt (uint256 x) internal pure returns (int128) {
unchecked {
require (x <= 0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF);
return int128 (int256 (x << 64));
}
}
/**
* Convert signed 64.64 fixed point number into unsigned 64-bit integer
* number rounding down. Revert on underflow.
*
* @param x signed 64.64-bit fixed point number
* @return unsigned 64-bit integer number
*/
function toUInt (int128 x) internal pure returns (uint64) {
unchecked {
require (x >= 0);
return uint64 (uint128 (x >> 64));
}
}
ABDK mul 函数代码
二进制中使用位运算作为 wad,乘法示例如下:
function mul (int128 x, int128 y) internal pure returns (int128) {
unchecked {
int256 result = int256(x) * y >> 64;
require (result >= MIN_64x64 && result <= MAX_64x64);
return int128 (result);
}
}
Uniswap V2 定点库
Uniswap V2 的定点库非常简单,因为 Uniswap V2 对定点数执行的唯一操作是将定点数加法和除法与整数相加或相除。
pragma solidity =0.5.16;
// a library for handling binary fixed point numbers (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Q_(number_format))
// range: [0, 2**112 - 1]
// resolution: 1 / 2**112
library UQ112x112 {
uint224 constant Q112 = 2**112;
// encode a uint112 as a UQ112x112
function encode(uint112 y) internal pure returns (uint224 z) {
z = uint224(y) * Q112; // never overflows
}
// divide a UQ112x112 by a uint112, returning a UQ112x112
// x * d / y
function uqdiv(uint224 x, uint112 y) internal pure returns (uint224 z) {
z = x / uint224(y);
}
}
encode() 函数将输入 uint112乘以定点数 Q112, 输出定点数 uint224
uqdiv() 函数只是将定点数除以整数,不需要额外的步骤。
Uniswap 使用此库来累积下方的 TWAP 预言机的价格。每次更新时,TWAP 都会将最新价格添加到累加器中(用于计算平均价格,但需要额外的步骤,这超出了本文的讨论范围)。由于价格以分数表示,因此定点数是理想的表示方式。
变量 _reserve0 和 _reserve1 保存池中最新的代币余额,并且是 uint112
price0CumulativeLast 和 price1CumulativeLast 是 UQ112x112
uniswap 中的 _update() 函数使用 UQ112X112 编码函数
function _update(uint balance0, uint balance1, uint112 _reserve0, uint112 _reserve1) private {
require(balance0 <= uint112(-1) && balance1 <= uint112(-1), 'UniswapV2: OVERFLOW');
uint32 blockTimestamp = uint32(block.timestamp % 2**32);
uint32 timeElapsed = blockTimestamp - blockTimestampLast; // overflow is desired
if (timeElapsed > 0 && _reserve0 != 0 && _reserve1 != 0) {
// * never overflows, and + overflow is desired
price0CumulativeLast += uint(UQ112x112.encode(_reserve1).uqdiv(_reserve0)) * timeElapsed;
price1CumulativeLast += uint(UQ112x112.encode(_reserve0).uqdiv(_reserve1)) * timeElapsed;
}
reserve0 = uint112(balance0);
reserve1 = uint112(balance1);
blockTimestampLast = blockTimestamp;
emit Sync(reserve0, reserve1);
}
向上舍入与向下舍入
定点库通常具有在除法时向上舍入的选项。例如,Solady 具有:
mulWadUp— 将两个定点数相乘,但除以d时向上舍入
/// @dev Equivalent to `(x * y) / WAD` rounded up.
function mulWadUp(uint256 x, uint256 y) internal pure returns (uint256 z) {
/// @solidity memory-safe-assembly
assembly {
z := mul(x, y)
// Equivalent to `require(y == 0 || x <= type(uint256).max / y)`.
if iszero(eq(div(z, y), x)) {
if y {
mstore(0x00, 0xbac65e5b) // `MulWadFailed()`.
revert(0x1c, 0x04)
}
}
z := add(iszero(iszero(mod(z, WAD))), div(z, WAD))
}
}
Reference
https://www.rareskills.io/post/solidity-fixed-point
https://github.com/abdk-consulting/abdk-libraries-solidity/blob/master/ABDKMath64x64.sol
https://github.com/transmissions11/solmate/blob/main/src/utils/FixedPointMathLib.sol
https://github.com/Vectorized/solady/blob/main/src/utils/FixedPointMathLib.sol